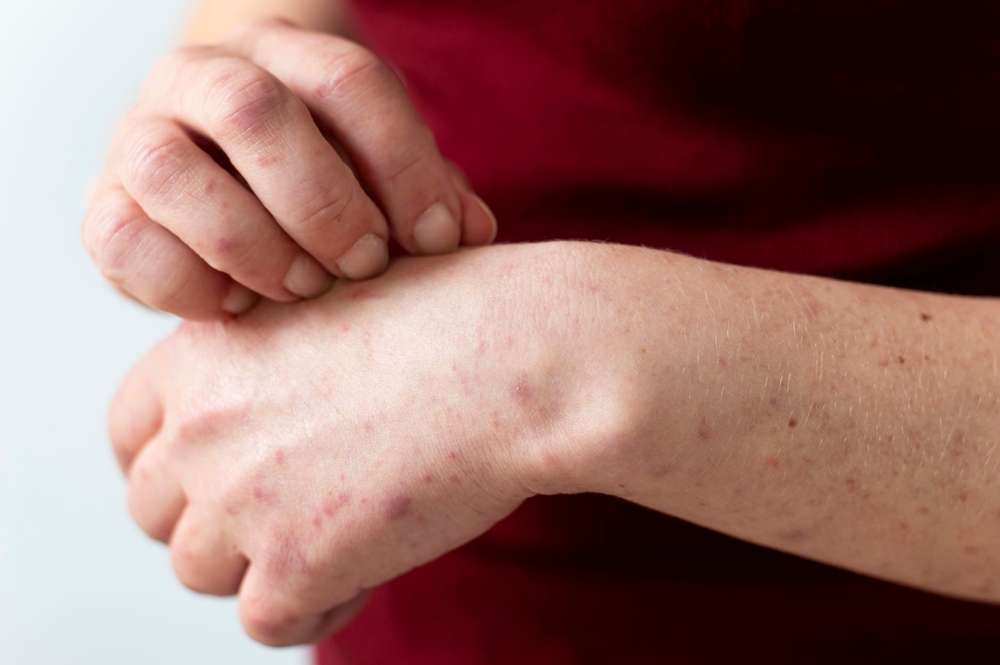
If you experience these symptoms, you may need to learn about Crohn's disease.
If you have recently experienced recurring abdominal discomfort, abnormal bowel movements, or chronic fatigue without a clear cause, these bodily signals may not be ordinary gastrointestinal problems. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that is not uncommon in the United States, and early symptoms are easily overlooked. Understanding common symptoms and disease characteristics can help identify risks early and seek professional evaluation at the appropriate time.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What symptoms might be associated with Crohn’s disease?
Crohn’s disease can manifest with a variety of symptoms, which often depend on the location and severity of the inflammation within the digestive tract. Common indicators include persistent abdominal pain, which can range from mild cramping to severe discomfort, often in the lower right abdomen. Chronic diarrhea, sometimes with blood or mucus, is another hallmark symptom. Individuals may also experience unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and fever. Less common but significant symptoms can include mouth sores, skin lesions, joint pain, and eye inflammation. The nature of these symptoms can vary greatly among individuals, making diagnosis complex.
Why are these symptoms easily mistaken for ordinary gastrointestinal problems?
Many of the initial symptoms of Crohn’s disease, such as abdominal pain and diarrhea, are common to a wide range of less serious gastrointestinal issues. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), food poisoning, or even simple dietary sensitivities can present with similar discomfort. This overlap often leads to delays in diagnosis, as individuals might initially dismiss their symptoms as temporary or manageable with over-the-counter remedies. The intermittent nature of Crohn’s disease, where symptoms may flare up and then subside, can further contribute to this confusion, making it difficult to recognize a chronic underlying condition.
What signals might the body be sending when symptoms persist or recur?
While occasional gastrointestinal upset is normal, persistent or recurring symptoms warrant closer attention, as they could signal a more significant underlying issue like Crohn’s disease. Key signals include symptoms that do not resolve on their own, worsen over time, or return frequently. Unexplained weight loss despite a normal diet, persistent fatigue that isn’t relieved by rest, and a low-grade fever without an apparent cause are particularly concerning. The body may also send signals through complications such as anemia due to chronic blood loss or nutrient malabsorption, or the development of fistulas or strictures in the digestive tract, indicating advanced inflammation.
How do doctors in the United States typically further evaluate these symptoms?
When persistent gastrointestinal symptoms suggest a potential chronic condition, doctors in the United States typically begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Initial diagnostic steps often include blood tests to check for signs of inflammation (like C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate), anemia, and nutritional deficiencies. Stool samples may be analyzed for occult blood, infection, or markers of inflammation. Imaging studies, such as CT scans, MRI enterography, or capsule endoscopy, help visualize the digestive tract. The definitive diagnosis often relies on endoscopic procedures like colonoscopy or upper endoscopy, which allow direct visualization of the intestinal lining and collection of tissue biopsies for microscopic examination by a pathologist.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Gastroenterologist | Diagnosis, treatment planning, ongoing management | Specializes in digestive system disorders, performs endoscopies |
| Registered Dietitian | Nutritional counseling, dietary adjustments | Helps manage symptoms through diet, addresses deficiencies |
| Colorectal Surgeon | Surgical intervention for complications | Specializes in bowel surgery, addresses strictures, fistulas |
| Pathologist | Tissue analysis from biopsies | Confirms diagnosis through microscopic examination of samples |
The importance of early disease understanding for long-term life management
Early recognition and understanding of Crohn’s disease are paramount for effective long-term management and improving the quality of life for individuals. A timely diagnosis allows healthcare professionals to initiate appropriate treatment strategies, which can include medications to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and prevent flare-ups. Early intervention can also help in preventing or mitigating serious complications such as intestinal blockages, fistulas, abscesses, and the need for surgery. Furthermore, understanding the disease enables individuals to actively participate in their care, make informed lifestyle choices, and work collaboratively with their healthcare team to develop a personalized management plan that addresses their specific needs and challenges.
Recognizing the diverse and often subtle symptoms of Crohn’s disease is a crucial first step toward managing this chronic condition. While initial signs may mimic common digestive issues, persistent or recurring symptoms warrant professional medical attention. Early evaluation and diagnosis are key to developing an effective treatment plan, preventing complications, and supporting a better quality of life for those affected by Crohn’s disease.