2025 Consumer Research: Three Truths You Should Know About Modern Hearing Aids
In 2025, hearing aid technology has evolved far beyond simple amplification into a new era of intelligent acoustics. Many individuals still hesitate to seek help due to outdated concerns about bulky designs or poor performance in noisy crowds. However, this year's research reveals a major shift: modern devices now feature near-invisible profiles and AI chips that prioritize human speech over background noise. This report details the three essential truths of the current market—covering discreet micro-designs, advanced sound filtering, and the rise of accessible OTC options—to help you navigate today's standards and reconnect with the sounds of your life.
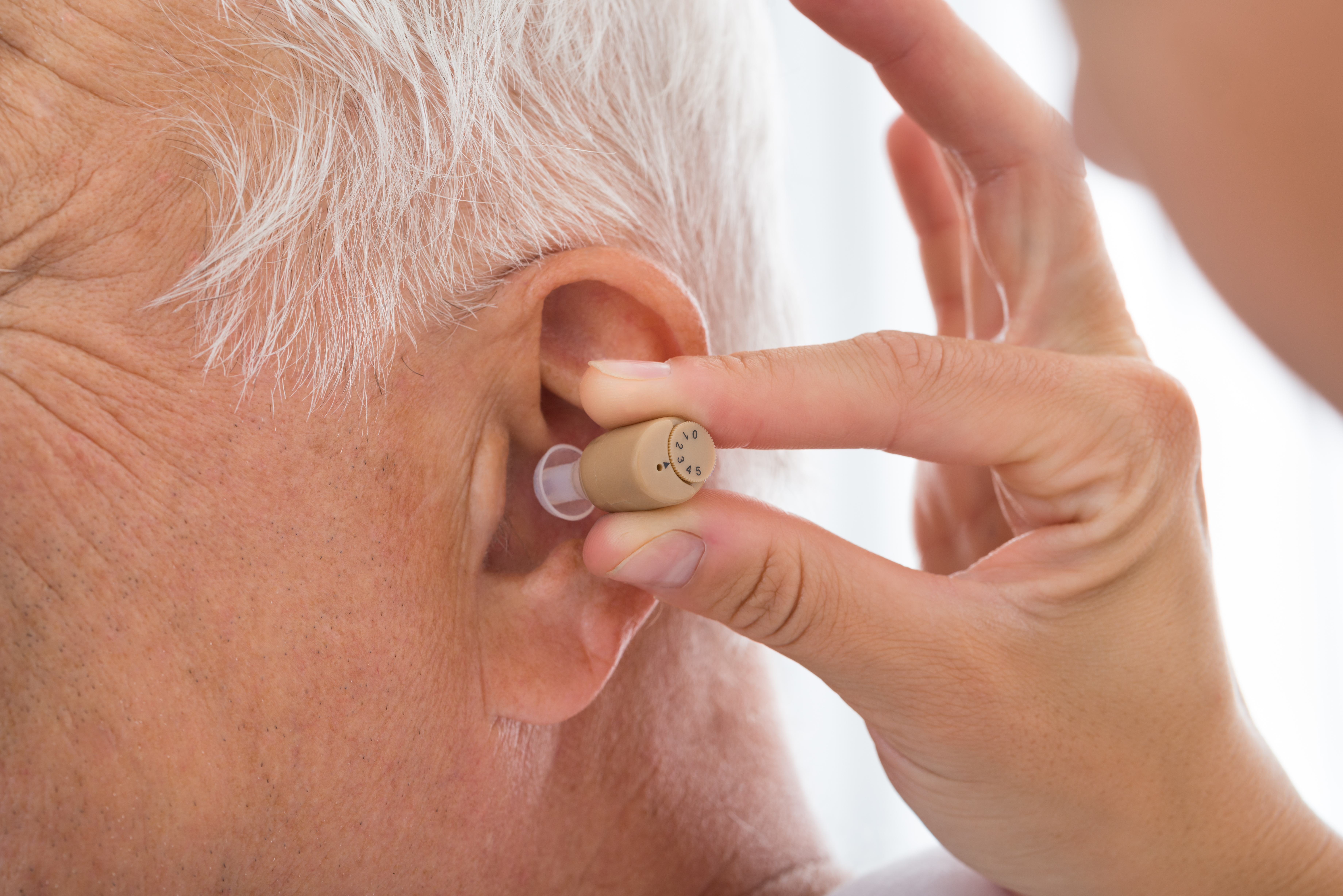
Hearing loss affects approximately 48 million Americans, yet only a fraction of those who could benefit from hearing devices actually use them. Misconceptions about size, functionality, and accessibility have historically created barriers. However, recent technological advances and regulatory changes have revolutionized the hearing aid landscape, making effective solutions more attainable for consumers across the country.
Clear Hearing is the Best Gift for Your Life
The ability to hear clearly impacts every aspect of daily living, from personal relationships to professional success and overall quality of life. Research consistently shows that untreated hearing loss correlates with social isolation, cognitive decline, and decreased earning potential. Addressing hearing challenges early can preserve neural pathways responsible for processing sound and speech comprehension. Clear hearing enables you to participate fully in conversations, enjoy entertainment, remain alert to environmental sounds, and maintain independence as you age. The emotional and psychological benefits extend beyond the individual, strengthening family connections and reducing caregiver burden. Modern hearing technology provides an opportunity to reclaim these experiences, offering customizable solutions that adapt to various listening environments and personal preferences.
Modern Hearing Aids: Smaller Than a Bean
One of the most significant advancements in hearing technology involves miniaturization. Contemporary hearing devices have shrunk to remarkably compact sizes, with some models measuring smaller than a coffee bean. This dramatic size reduction results from innovations in microelectronics, battery technology, and acoustic engineering. Completely-in-canal and invisible-in-canal devices sit deep within the ear canal, making them virtually undetectable to others. Even behind-the-ear models have become sleeker and more discreet, often hidden by hair or blending naturally with skin tones. The smaller form factor does not compromise performance; these devices pack sophisticated processing power into tiny packages. Rechargeable options eliminate the need for frequent battery changes, while wireless connectivity enables seamless integration with smartphones and other devices. The cosmetic improvement addresses a primary concern that previously prevented many people from seeking hearing assistance, removing the stigma associated with visible hearing devices.
A Smart Brain: Hearing Voices Not Noise
Modern hearing devices incorporate artificial intelligence and advanced signal processing to distinguish between speech and background noise. This smart technology analyzes incoming sounds in real time, amplifying voices while suppressing unwanted environmental noise. Machine learning algorithms adapt to your listening preferences and environments, creating personalized hearing profiles that improve over time. Directional microphones focus on sounds coming from specific directions, particularly useful in crowded restaurants or social gatherings. Some devices feature multiple listening programs that automatically switch based on your surroundings, whether you are in a quiet room, outdoors, or in a noisy venue. Feedback cancellation technology eliminates the whistling sounds that plagued older models. Wind noise reduction improves outdoor experiences, while music programs preserve the richness of musical performances. These intelligent features work together to provide natural-sounding amplification that closely mimics healthy hearing, allowing you to focus on conversations without constant manual adjustments.
Understanding OTC Policy: Simpler Than Ever
Regulatory changes implemented in recent years have transformed hearing aid accessibility in the United States. The FDA established a category for over-the-counter hearing aids, allowing adults with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss to purchase devices directly without medical exams or professional fittings. This policy shift aims to increase affordability and availability while maintaining safety standards. OTC devices must meet specific performance and labeling requirements, ensuring consumers receive quality products. The regulation distinguishes between OTC options suitable for self-management and prescription devices requiring professional oversight for more severe hearing loss. This tiered approach provides flexibility, enabling consumers to choose solutions that match their needs and budgets. Many manufacturers now offer direct-to-consumer models with online hearing assessments, smartphone apps for self-adjustment, and telehealth support. While professional audiological care remains valuable for comprehensive hearing evaluation and complex cases, the OTC pathway removes traditional barriers for those seeking initial intervention.
| Device Type | Provider Examples | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| OTC Hearing Aids | Eargo, Lively, Audicus | $500 - $1,500 per pair |
| Prescription Behind-the-Ear | Phonak, Oticon, Widex | $2,000 - $6,000 per pair |
| Prescription In-the-Ear | Starkey, ReSound, Signia | $2,500 - $7,000 per pair |
| Personal Sound Amplification | Various retailers | $50 - $500 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The cost of hearing devices varies significantly based on technology level, features, and whether you choose OTC or prescription options. Entry-level OTC devices start around five hundred dollars per pair, while premium prescription models with advanced features can exceed seven thousand dollars. Many prescription hearing aids include professional services such as initial fitting, follow-up adjustments, and ongoing support, which contribute to higher prices. Some insurance plans and Medicare Advantage policies provide partial coverage, though traditional Medicare does not cover hearing aids. Financing options and payment plans are commonly available through providers and manufacturers. When evaluating costs, consider the total value including warranty coverage, repair services, and expected device lifespan, which typically ranges from three to seven years.
The hearing aid industry continues evolving rapidly, with ongoing innovations in connectivity, battery life, and artificial intelligence. Consumers now have unprecedented choice in device styles, purchasing methods, and price points. Whether you select an OTC device for convenience and affordability or work with an audiologist for a fully customized solution, modern hearing technology offers effective options for improving your hearing health. The combination of smaller sizes, smarter processing, and simplified access has removed many traditional obstacles, making it easier than ever to address hearing challenges and maintain your quality of life.




